0%
回溯
发表于:
分类于:
Leetcode/Backtracking
Linked List
发表于:
分类于:
Leetcode/LinkedList
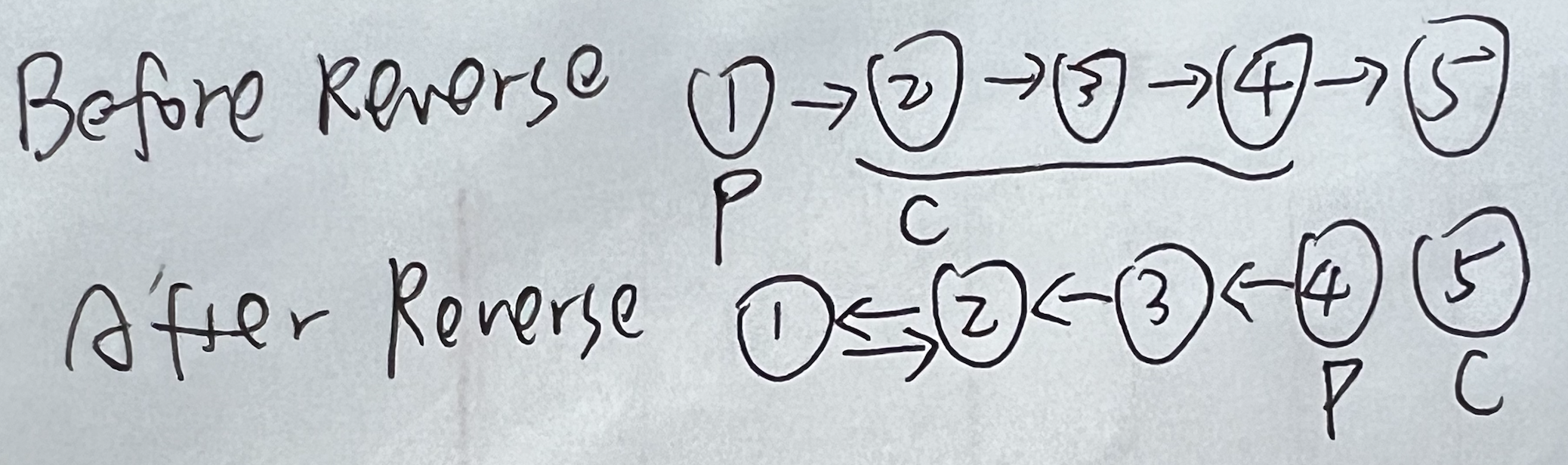
反转链表
| |
反转链表关注 pre和cur在开始前和结束后的位置,在这一题中,旧pre的next为新的pre,旧cur的 next为新的cur.
Spring
发表于:
分类于:
Spring
BeanFactory Interface
| |
可以发现ConfigurableApplicationContext接口继承了BeanFactory接口
 这个context里面包含了一个beanFactory变量。
这个context里面包含了一个beanFactory变量。
Java 8的新特性
发表于:
分类于:
Java/Basic
达人探店
发表于:
分类于:
BlackHorse Rating
接口和抽象类
发表于:
分类于:
Java/Basic
Interface
接口是对行为的抽象。
- abstract method, Java 8以前接口只能有抽象方法
- default method,提供方法体,Java 8 以后有
- static method, 提供方法体,Java 8 以后有,可以通过Interface.method()调用
| |
Abstract Class
抽象类通常作为基类,比如 Person,Animal。因为不同子类的某种方法的 body可能不一样,所以把这些方法作为abstract method放在抽象类中。
Concurrency
发表于:
分类于:
Operating System
黑马点评商户缓存
发表于:
分类于:
BlackHorse Rating
优惠券秒杀
发表于:
分类于:
BlackHorse Rating
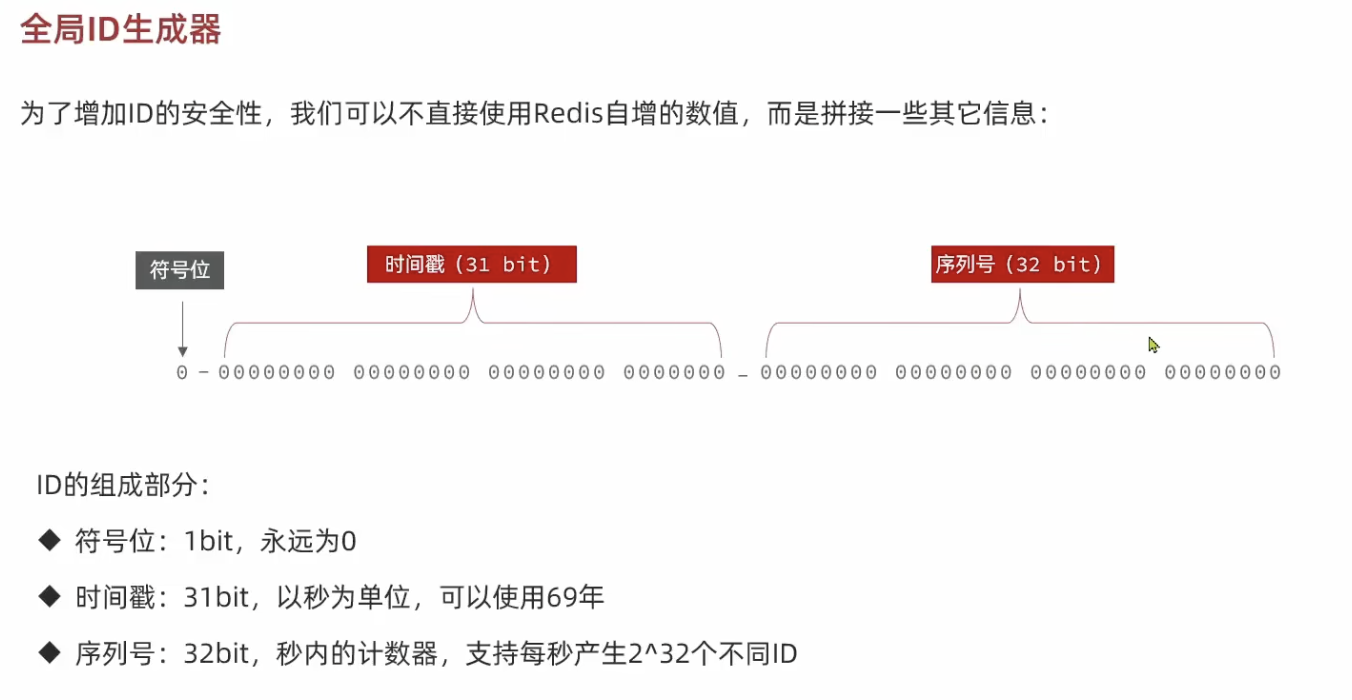
全局ID生成器: Redis自增
使用数据库自增ID的缺点:
- 可能会暴露给用户一些信息:用户可能会根据此推断,一天之内销售出了多少张优惠券。
- 当优惠券太多时,会导致数据库ID过大。但如果为优惠券分表,又会出现许多优惠券共用同一个ID的情况。

| |
这里的 keyPrefix表示一种object,比如优惠券订单