MySQL Logs
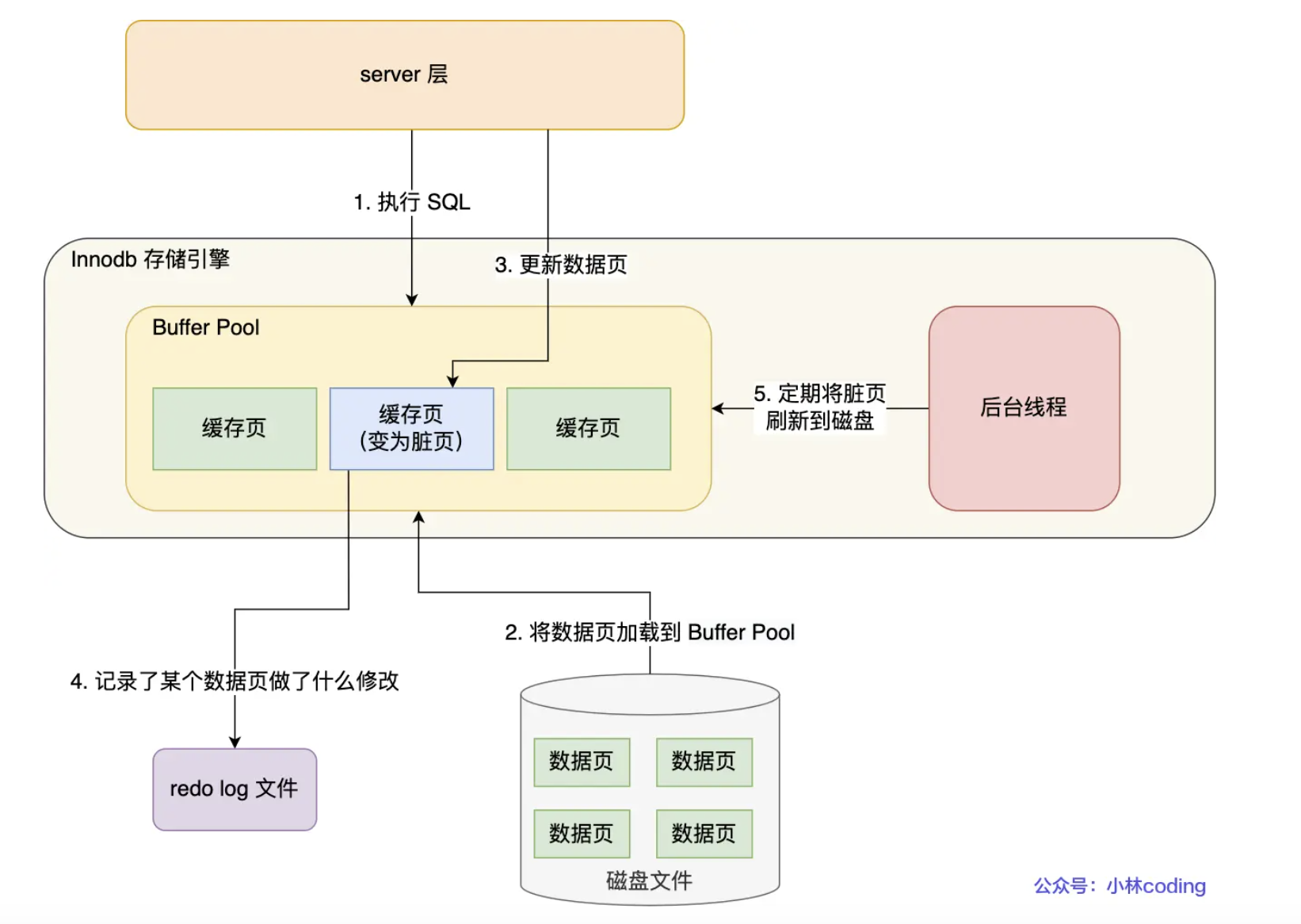
All DML operations (INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) are first performed in the Buffer Pool.
Redo Log
- Provides transaction durability. Redo log is flushed first; dirty pages are flushed later.
Physical Storage Characteristics
File structure
- Fixed-size files (e.g., ib_logfile0, ib_logfile1)
- Circular write (ring buffer)
- Physical appends are always to the end of file
Write pattern
| |
Write-Ahead Logging (WAL)
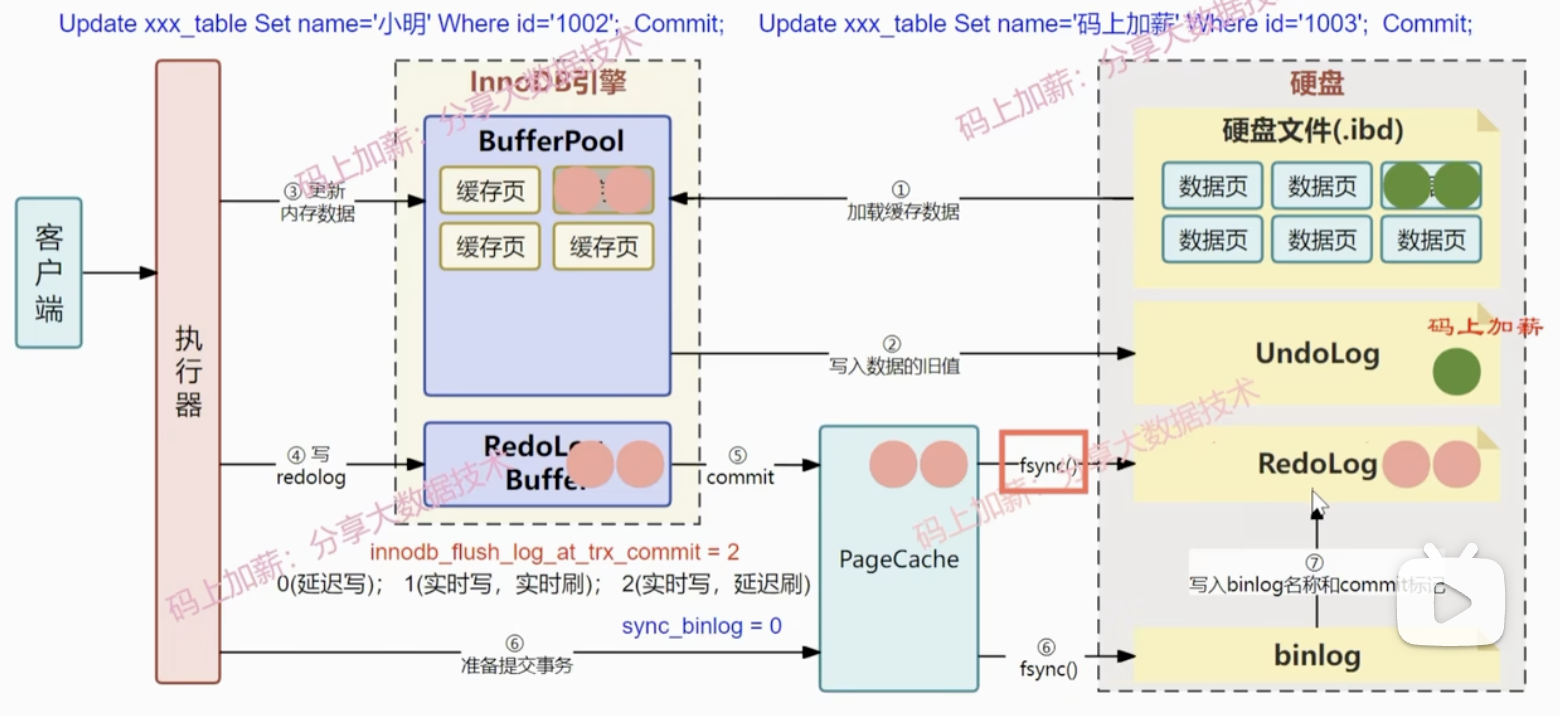
- Update data pages in the Buffer Pool; the page becomes a dirty page.
- Write the physical changes (e.g., “page X, offset Y, write Z”) sequentially to the redo log buffer.
- On COMMIT, behavior depends on innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit (commonly 1 by default):
| Value | Behavior | Durability |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (default) | 1) write to OS page cache; 2) fsync() immediately | Full durability |
| 0 | Batch write+fsync every 1s | May lose up to 1s of data |
| 2 | Write to OS page cache but delay fsync | Safe unless OS crashes |
- Dirty page flushing is asynchronous; background threads flush Buffer Pool pages to disk.
Undo Log
- Enables transaction rollback to ensure atomicity
- Works with ReadView to implement MVCC, maintaining a version chain for each record
Binlog
Basics
Binlog (Binary Log) is the MySQL Server-layer binary log that records all data changes as logical events; entries are written when a transaction commits.
Key Properties
What it records:
- All DDL (CREATE/ALTER/…) and DML (INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE)
- Stored as events with metadata like execution time and error codes
Binlog vs Redo Log
Binlog Redo Log Layer Server layer InnoDB engine layer Type Logical (SQL/events) Physical (page changes) Purpose Replication/point-in-time restore Crash recovery Formats:
- STATEMENT: records original SQL (may cause replica divergence due to environment differences)
- ROW: records row-level changes (recommended default)
- MIXED: hybrid mode
Replication
server-id uniquely identifies a MySQL instance; both primary and replicas must have one and they must be distinct, to differentiate nodes.
The primary opens a thread to distribute binlog events, called the Binlog Dump thread.
On the replica there are two key threads: an I/O thread that connects to the primary, requests binlog events, and writes them to the relay log; and an SQL thread that reads the relay log and replays it to update data on the replica.
Primary parameters
log-bin enables the binary log, and binlog-format sets the format.
Replica parameters
- Master_Host: primary’s IP
- Master_User: replication user
- Master_Port: port
- Master_Log_File: current binlog file name on the primary