Linked List
Reverse Linked List
| |
Reverse linked list focuses on pre and cur positions before start and after end. In this case, old pre.next becomes new pre, old cur.next becomes new cur.
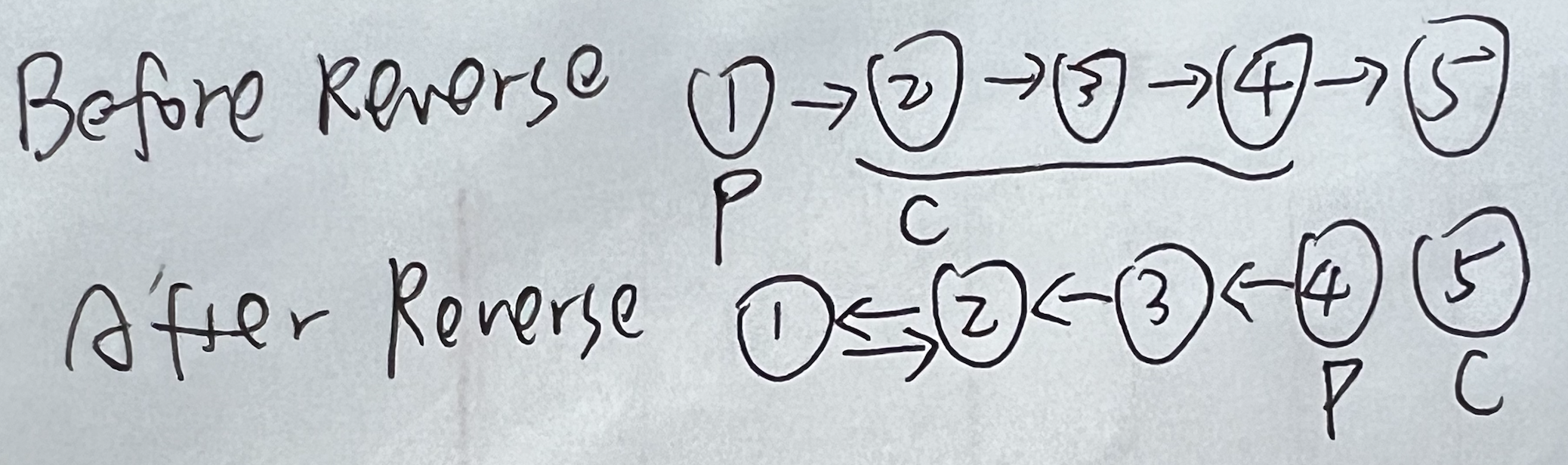
If reversing entire list, return pre at end.
- Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Fast-Slow Pointers
Find middle node, detect cycles.
This approach: with 4 nodes, slow ends at third node.
If initialize fast=head.next, slow ends at second node.
| |
If initialize fast=head.next, slow gets exact middle node. For 8 nodes, slow at fourth node.
LC 143 (Fast-Slow Pointers + Reverse List)
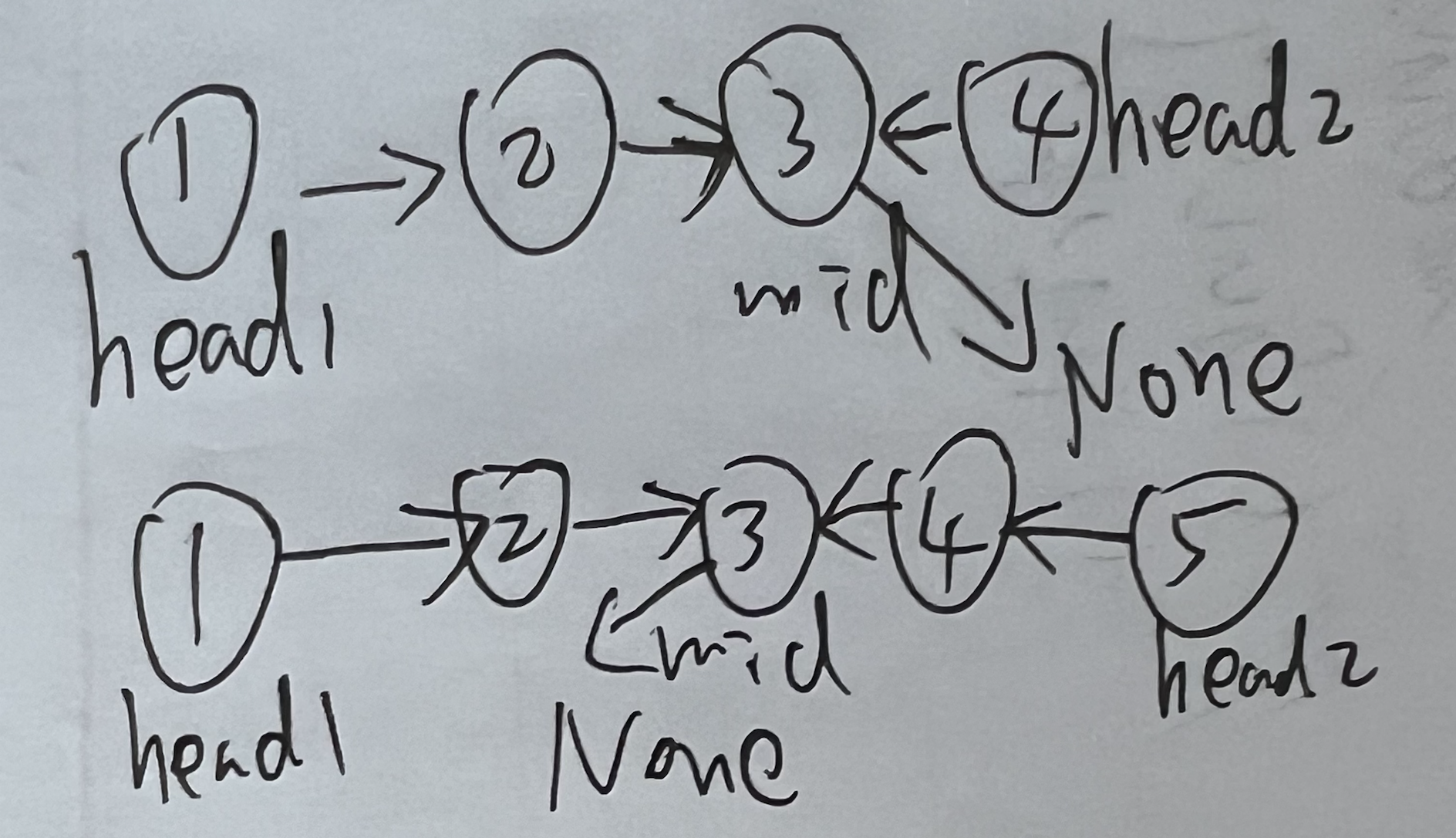 Find middle node mid, reverse everything after mid. From result, these pointers need reversal.
Diagram shows reversed result. Then repeatedly set head1.next=head2, head2.next=head1.
Observation: whether odd or even list, loop can end when head2.next is None.
Find middle node mid, reverse everything after mid. From result, these pointers need reversal.
Diagram shows reversed result. Then repeatedly set head1.next=head2, head2.next=head1.
Observation: whether odd or even list, loop can end when head2.next is None.
Copy Random Linked List
TODO
LC 146. LRU Cache
Doubly linked list → O(1) insert and delete nodes dict → key as key, value as Node
Helper functions: remove(node), get_node(key)→node (return node and move to front: remove then push_front), push_front(node)
Can maintain dummy.pre as last node since push_front modifies dummy.pre
LC 106. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
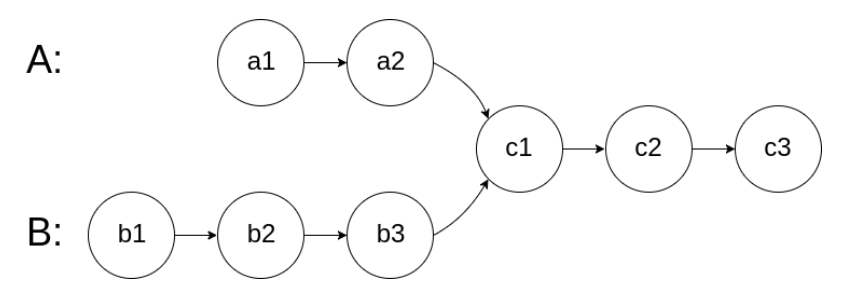 Let A list own part length x, B list own part length y, common part length z.
Idea: pointers from A and B both travel distance x+y+z, they meet at node c1.
Let A list own part length x, B list own part length y, common part length z.
Idea: pointers from A and B both travel distance x+y+z, they meet at node c1.